What Is Edge Computing? 8 Examples and Architecture You Should Know

Overviews
- What is Edge Computing?
- How Does Edge Computing Work?
- 7 Benefits of Edge Computing
- Edge Computing Examples and Use Cases
- Edge Computing Architecture Overview
- Relationship between Edge Computing Equipment and Power Supply Units
- Edge Computing, IoT, and 5G Possibilities
- FSP's Edge Computing Power Supply Solutions
Author: FSP Group
| Edge Computing Application and Solutions |
With the rapid advancement of 5G, AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing has become a critical technology for enabling real-time data processing and intelligent applications. In our daily lives, numerous devices and microservers are interconnected through high-speed fiber-optic networks, forming a distributed computing network that functions much like a vast data center — this is edge computing.
To ensure the stable operation of these devices, high-efficiency and reliable power supplies are indispensable. This article explores the principles of edge computing, its application scenarios, and the crucial role power supplies play in maintaining system performance and stability.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is the process of storing individual user data as near to the source as possible. This could be at the periphery, or the edge, of an associated network. Many opportunities arise for the positioning of servers at the edge of a network, as well as data storage and processors. Due to the fact this data is closer to the user, it means it minimizes latency. This is a distributed I.T. network that ultimately leverages the minimal distance required. It increases the speed of service, and this generates the associated heightening of value.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Location is the primary concern in edge computing. Due to the rapid rise of devices and the amount of data being transferred through the Internet, traditional data centers are struggling to keep up. Therefore, the focus is now being targeted to the infrastructure’s logical edge, relocating resources to the point of data generation. In essence, instead of data traveling to the data center, the data center is repositioned closer to the data. However, closer does not necessarily mean physically closer, it means closer in terms of the network and routing. Depending on the number of service providers a business utilizes, such as the cloud, etc., there could be many systems all potentially able to be the edge. Nevertheless, storage and servers are set up where the data is. All this requires is a small amount of computing setup to operate a remote LAN. Computing gear is applied to the network and protected against environmental factors in various ways. When the data is processed, the data stream is normalized and analyzed for business intelligence. The results of this are the only pieces of data that are rerouted back to the main data center.
7 Benefits of Edge Computing
There are many benefits of edge computing as it targets problems in the existing infrastructure:
-
Autonomy
It processes data on a local network reducing the sheer amount of data that needs to be sent and received. This means you need less bandwidth and connectivity time.
-
Data jurisdiction
By keeping data close to the source, there are fewer problems associated with the crossing of national borders, boundaries, and sovereign laws. This means that edge computing creates fewer legal issues, including security and privacy.
-
Security
Edge deployment allows data to be encrypted when it travels to the cloud or to the data center. Also, edge computing can be strengthened against cybercrime, such as hacking. This is even possible if the IoT devices are limited in terms of security capability.
-
Minimal latency
Due to processors being available close to where the data will be used improves processing time. It also enables real-time analytics. The opportunities for new markets are exponential.
-
Simplified maintenance
Micro-data centers (µDC) are tiny, can be transported on the back of a truck, and are created with as much accessibility and modularity as possible.
-
Reduced cooling costs
Large data centers can cost a lot to cool. However, cooling a range of smaller data centers could cost a lot less, at least in theory.
-
Climate consciences
It is possible that many smaller data centers will use less energy than one huge data center if edge could appropriately maximize accuracy and efficiency within its computerizations.
Edge Computing Examples and Use Cases
In today's world of fast-paced technology, edge computing has gained significant attention. Here are some of the edge computing examples that are being implemented across various industries:
-
Healthcare & Patient Monitoring
Edge computing is being used in the Healthcare industry. Medical devices generate vast amounts of data that need to be processed quickly and efficiently. By deploying edge computing, healthcare providers can process this data at the edge of the network, allowing for faster diagnosis and treatment.
Also, there are several in-hospital opportunities for edge computing. First, it would mean that there is less need for third-party storage systems. By processing data locally, there is more patient privacy. It would also mean that there would be better notifying of patient vitals. In addition, it would create a complete view of patients’ dashboards.
-
Smart Homes
Implementing edge technology in smart homes offers a more feasible solution than traditional systems that rely on sending and receiving data to and from a main storage hub. This approach not only reduces latency, but also enhances security while minimizing backhaul costs. As a result, voice commands are executed more quickly and in real-time, providing a seamless and efficient experience for users.
-
Smart Cities
Edge computing is also being used to create Smart Cities. By deploying edge computing devices across the city, local authorities can monitor traffic, air quality, and other environmental factors in real-time. This approach can help them identify and respond to issues quickly, improving the overall quality of life for citizens.
-
Traffic Management
As road traffic continues to increase, the need for smarter traffic management systems becomes more pressing. Edge computing can be instrumental in optimizing traffic flow in cities by dynamically opening up lanes where and when necessary, and it will play a crucial role in managing the movement of autonomous vehicles.
-
Manufacturing & Smart Factory
Manufacturing industries are using edge computing to improve their operations, such as:-
Effective accelerating platform data communication:
Edge computing plays a vital role in accelerating data communication between different types of machinery in the manufacturing process. By integrating digital and physical technologies, edge computing enables faster and more flexible responses to various situations. This technology also facilitates the construction of a scalable and flexible platform by integrating predictive analysis and machine learning algorithms. Overall, edge computing helps to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of data communication in manufacturing processes.
-
Facilitating machine maintenance and parameter adjustment:
Machine automation is the key to the success of manufacturing industries. The Internet of Things (IoT) is utilized to detect and monitor machine operations, while edge computing is employed to analyze on-site data. When an anomaly is detected, workers can make corrections or implement predictive maintenance in advance to prevent it from affecting the production line. This data also helps manufacturers analyze the indicators that affect machine operation the most, extend machine life, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance machine operating efficiency.
-
-
Self-Driving Cars
Edge computing plays a crucial role in the development of autonomous vehicles. It enables real-time response to traffic situations: In general, it takes about 100ms to transmit data from the car sensor to the back-office cloud data center, and the transmission time may increase as the data volume increases. In terms of driving decision-making, data transmission delays may significantly affect the situated response of self-driving cars. Hence, edge computing can help resolve the data transmission delay among data centers to enhance driving safety.
-
Crowd Management
Edge computing is essential for managing large events, such as concerts and matches. It facilitates crowd control by enabling mobility applications to program messages for each attendee regarding ticket purchase, transportation routes, entrance or seat locations, and exclusive event content. Additionally, edge computing helps organizers understand attendee mobility and engagement, allowing them to make informed decisions such as launching flash sales.
-
Distributed Grid Management
As more electricity subscribers from different sectors and power plants adopt distributed regional grids over central generation, the demand for a large volume of real-time data and synchronization increases. Edge computing and energy storage systems can help achieve distributed grid management and optimize grid balance. This technology also enables energy conservation, such as reducing costs for high energy-consuming production activities and protecting the environment. By enhancing electricity efficiency in households, factories, cities, and countries, edge computing enables user-centered electricity service and provides more data for proper resource utilization.
-
Logistics
Logistics is another industry that is using edge computing to improve their operations. By deploying edge computing devices in warehouses and shipping centers, logistics companies can monitor inventory levels, track shipments in real-time, and optimize routes. This approach can help them reduce delivery times, lower costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
-
Security
Edge computing has proven to be a game-changer in various domains, and security is no exception. One such application of edge computing technology is in ensuring worker safety in hazardous work environments. The data collected from devices like onsite cameras, safety devices, and sensors are crucial in achieving this objective. These devices help in preventing unauthorized access to the site, and they also monitor the safety protocols followed by the employees. In the event of a safety breach or a potential hazard, the data collected by these devices can alert the concerned authorities in real-time. This timely response can help in averting a disaster and ensuring the well-being of workers.
Edge technology has numerous useful applications, and the examples listed above are just a few of them.
Edge Computing Architecture Overview
After understanding the benefits and usage of edge computing, you would be able to see how edge computing and its applications can be found almost everywhere in our daily life. But do you know what edge computing architecture consists of and what key layers are involved?
A typical edge computing architecture can be divided into three layers: The cloud layer, or the layer that is responsible for processing and storing all data; The edge layer, or the layer that handles the data processing near real time; And the device layer, or the layer that is in charge of detecting and performing simple processing. Let’s demystify the three layers in the edge computing architecture in the following paragraphs.
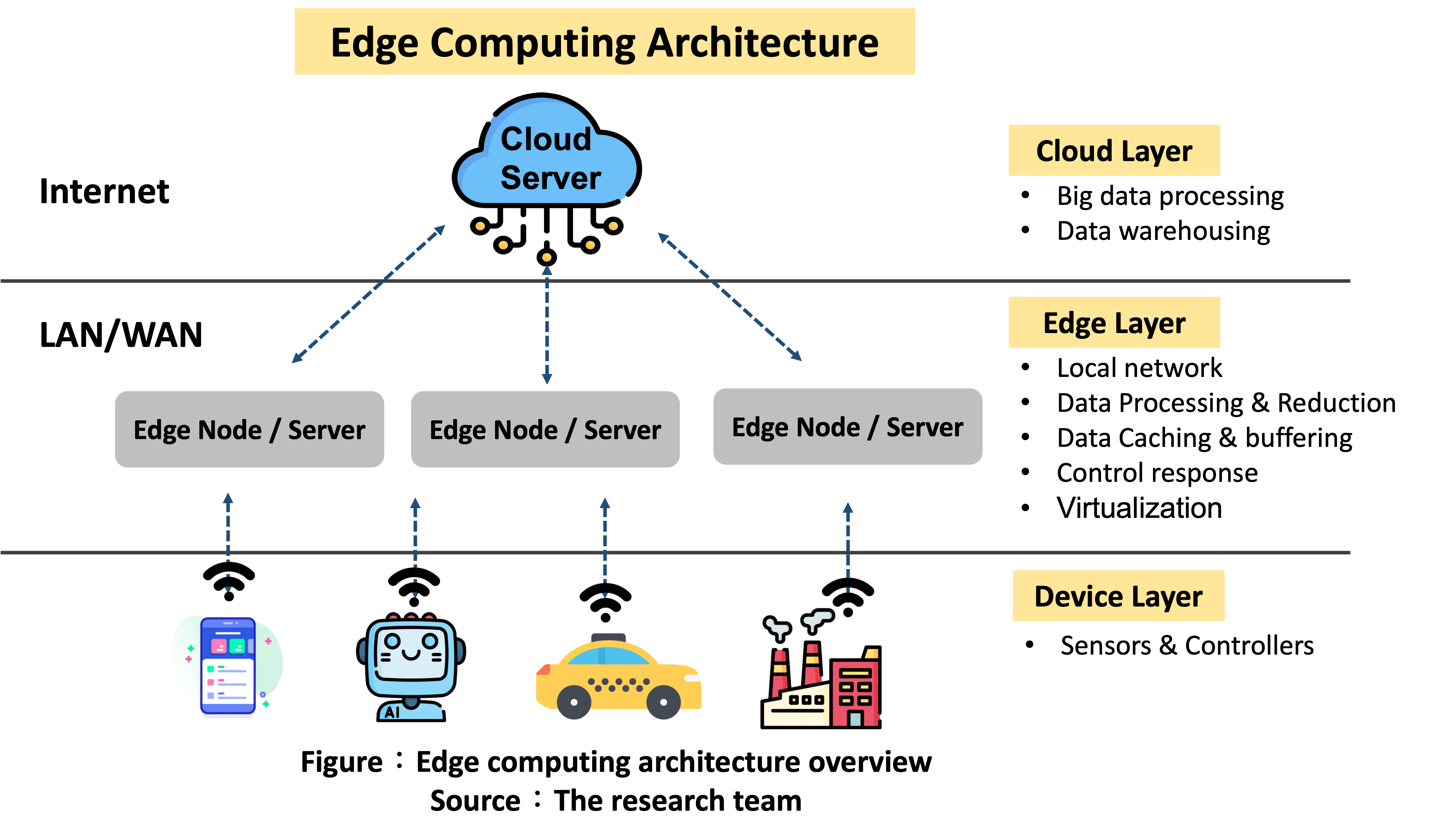
Figure: Edge computing architecture overview
Cloud Layer
Although edge computing was introduced to address network congestion and latency problems commonly found in cloud computing, cloud computing in fact still plays an important role in the entire edge computing architecture. We can say that cloud computing and edge computing complement one another. Through the edge layer described in the next section, the entire system determines if data needs to be processed in the cloud layer. If that is the case, edge servers will pass data to the cloud layer for complex processing. On the other hand, edge servers will also pass a part or critical data to the cloud layer for storage and comprehensive analysis. This also demonstrates the integration between both the cloud and edge layers.
Edge Layer
This layer mainly consists of edge servers, and when compared to the cloud layer, the edge layer contains edge servers that are larger in quantity and more vastly deployed. Therefore, through distributed edge computing, the edge layer can process data that is closer to the data source and address latency problems found in cloud computing. The edge layer can be considered the core in the entire edge computing architecture. After data from the device layer is analyzed and processed in the edge layer, data is transmitted to the cloud layer for subsequent processing and analysis. Data which cannot be processed in the edge layer can be sent to and analyzed in the cloud layer to ensure data integrity.
Device Layer
Amongst the three layers, the device layer contains the most devices. Ranging from devices that are as small as our mobile phones or computers to ones that are as large as buses and factories, these devices are all examples of components in the device layer. Through their sensors, devices in the device layer collect and capture data used to help products achieve the purposes they are designed for. Equipment in a hospital collecting vital signs of patients and autonomous vehicles capturing data of other nearby vehicles are all such examples. Although components in the cloud and edge layers possess better computing power, the devices in the device layer can still perform data analyses, processing and storage tasks which require negligible computing power, as well as process data closest to the data source in almost real‑time.
Relationship between Edge Computing Equipment and Power Supply Units
In terms of edge computing equipment, power consumption is an inevitable issue. That is, the more functions there are, the higher the power consumption will be. In terms of electricity demand, as unreliable and dirty power sources are everywhere in the industrial IoT environment and some edge computing equipment is not in active mode, some applications will need energy storage systems to supply low power and an alternative power source. In terms of the wattage of power supply units (PSU), the equipment size and PSU size and wattage are proportional, i.e., the bigger the equipment is, the greater the wattage is required, and the larger the PSU size will be. For the edge computing unit to run more efficiently, unit design becomes simpler to shorten the response time. Hence, size reduction, efficiency enhancement, and thermal solution optimization have become the focus.
Effects of power supply units on edge computing performance
The OT deployment of edge computing is diverse in different sectors. In the manufacturing sector, the deployment focus is the protection and management of stationary industrial automation equipment. In the energy and utility sectors, remote access is the key to deployment. In the transportation, railway, mining, and agriculture sectors, mobility application is emphasized. Each section has its own standards and certification requirements to ensure the protection of the application of field-specific knowledge, best practices, and safety. Compared to the stable environment of traditional data centers, in response to the environment and hardware size of edge computing, the electricity efficiency, power density, and reliability of power supply units (PSUs) play an essential role. While “electricity” is the key, power disruption due to PSU instability is a prevalent, annoying issue. For example, whether or not power leakage when running at high voltage will affect hardware operation and even cause industrial safety issues when the load is high, or whether or not efficiency and stability of power supply can maintain the basic computing performance of equipment when the load is low. Although IT and the cloud environment can compensate for the defects in the former, hardware quality is still the major effect. While high-quality PSUs can prevent data loss, data distortion, and other issues in edge computing devices, for stabler and better performance of edge computing, quality PSUs are indispensable to edge computing.
Considerations of Choosing Power Supply in these Edge Computing Applications
One problem of edge computing may well be the need for power. It does not matter where the server is, it will require high-powered processors. Other considerations that will need to be made in reference to the power supply options include: installation location, input specification, operation temperature, IP rating (IEC60529) (IP - Ingress Protection), surge requirement, and power connectors. All these variables can affect the efficiency, effectiveness, and ability of the network to run continually, without any meaningful loss of power.
Edge Computing, IoT, and 5G Possibilities
Edge computing is an evolving entity with new technology being brought in all the time. All this enhances its availability, capabilities, and performance. More and more products are being specially made with edge technology. Decentralization of data is the future. 5G will have an effect on edge by increasing its capabilities, such as with the autonomy of vehicles. It will also make wireless networks much more flexible while reducing costs. Due to the fact that the IoT is still rapidly rising, it means that the development of edge computing will evolve alongside it. There will be scope for MMDCs (micro modular data centers) that are already in development and are about the size of a box. These MMDCs can be deployed close to where the data is needed.
FSP's Edge Computing Power Supply Solutions
FSP has many edge computing solutions in operation. They are equipped with appropriate multi-communication technology to enhance any network. They have the best power supply installed and many associated functions. You can easily connect with these data centers and analyze the data schematics to enhance your business functionality.

FSP has complete CRPS product line, suitable for cloud, edge computing and other application fields.
Related Articles
About FSP
FSP Group is one of the global leading power supply manufacturer. Since 1993, FSP Group has followed the management conception “service, profession, and innovation” to fulfill its responsibilities as a green energy resolution supplier.




